When you allow for multiple field values to be selected in a SSRS report there needs to be additional logic added to the back end to deal with this.
This is best explained with an example scenario.
I have a table called Ireland with two columns, ID_Column and County. You can use the script below to create and populate this table. Run the query below to follow the working example.
CREATE DATABASE [TEST_DB];
USE [TEST_DB];
GO
/****** Object: Table [dbo].[Ireland] Script Date: 07/15/2015 10:49:49 ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
SET ANSI_PADDING ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Ireland] (
[ID_Column] [int] IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL
,[County] [varchar](9) NULL
,PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([ID_Column] ASC) WITH (
PAD_INDEX = OFF
,STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF
,IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF
,ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON
,ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON
) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
GO
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ON
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (1, N'Antrim')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (2, N'Armagh')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (3, N'Carlow')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (4, N'Cavan')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (5, N'Clare')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (6, N'Cork')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (7, N'Derry')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (8, N'Donegal')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (9, N'Down')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (10, N'Dublin')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (11, N'Fermanagh')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (12, N'Galway')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (13, N'Kerry')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (14, N'Kildare')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (15, N'Kilkenny')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (16, N'Laois')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (17, N'Leitrim')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (18, N'Limerick')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (19, N'Longford')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (20, N'Louth')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (21, N'Mayo')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (22, N'Meath')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (23, N'Monaghan')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (24, N'Offaly')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (25, N'Roscommon')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (26, N'Sligo')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (27, N'Tipperary')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (28, N'Tyrone')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (29, N'Waterford')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (30, N'Westmeath')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (31, N'Wexford')
INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] ([ID_Column], [County]) VALUES (32, N'Wicklow')
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Ireland] OFF
If I wanted to allow a user to select every county from the Ireland table in an SSRS report I would create a stored procedure that simply executes the following query.
However an SSRS report which allows users to choose counties in Ireland like below means that a WHERE clause needs to be introduced and be able to respond to the field values selected.
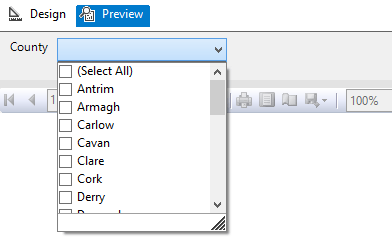
But the issue is that the SSRS report will pass the multi-valued parameter as a string with the values separated by a comma.
So instead of receiving the required: ‘Antrim’, ‘Armagh’, ‘Carlow’, ‘Cavan’ etc. for use in the WHERE clause.
SQL Server is passed: ‘Antrim, Armagh, Carlow, Cavan’ etc. which cannot be used.
So the first additional logic and code to be added to the back end to deal with the multi-value parameter is a User Defined Function (UDF) which splits the parameter. The following function and quotations are taken from the 4guysfromrolla website.
Function Scope:
“There are generally two parameters to a split function: the list to split and the character(s) to split on, the delimiter. In the following function we begin by declaring our input variables – @List, the list to split, and @SplitOn, the delimiter(s) to split on. The return value of this UDF is a table with two fields: Id, an identity column, and Value, an nvarchar(100) column.”
Function Logic:
“The main body of the function simply loops through the string finding the first occurrence of the delimiter on each pass. Once the delimiter has been found, the string is broken into two pieces. The first piece is inserted into the result table while the second piece replaces the original list. The loop continues until no more occurrences of the delimiter are found. Lastly, the remainder of the list is added to the result table. Return the table and you have a split function.”
Run the query below to follow the working example.
USE [TEST_DB];
GO
CREATE FUNCTION [dbo].[Split] (
@List NVARCHAR(2000)
,@SplitOn NVARCHAR(5)
)
RETURNS @RtnValue TABLE (
Id INT identity(1, 1)
,Value NVARCHAR(100)
)
AS
BEGIN
WHILE (Charindex(@SplitOn, @List) > 0)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @RtnValue (value)
SELECT Value = ltrim(rtrim(Substring(@List, 1, Charindex(@SplitOn, @List) - 1)))
SET @List = Substring(@List, Charindex(@SplitOn, @List) + len(@SplitOn), len(@List))
END
INSERT INTO @RtnValue (Value)
SELECT Value = ltrim(rtrim(@List))
RETURN
END
(For a line by line break down of the function please see the webpage.)
Now that the split function exits within the database it is now possible to use a Stored Procedure to SELECT from the Ireland table pulling back specific counties by way of a WHERE clause.
Run the query below to follow the working example.
USE Test_DB;
GO
IF OBJECT_ID('[GetCounties]') IS NULL
EXEC ('CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.[GetCounties] AS SELECT 1')
GO
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetCounties] @County VARCHAR(MAX)
AS
/*
NAME OF SP: GetCounties
Author: Bloggins86
Date: 15/07/2015
Purpose: Test multi-parameter select
*/
------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------
--INSERT STORED PROCEDURE LOGIC HERE
SELECT *
FROM Ireland
WHERE County IN (SELECT Value FROM dbo.Split(@County, ','))
------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------
Now that the populated table, split function and county select SP exists run the query below passing a string with multiple counties to return Dublin, Meath and Cork from the Ireland Table.
EXEC dbo.[GetCounties] 'Dublin, Meath, Cork'
You should now have returned the table with Dublin, Meath and Cork as separate row entries.
And that’s it, thanks for reading.


